Hydrogen storage alloy
Looking ahead to a society prioritizing the reduction of carbon emission, we established our hydrogen storage technology from an early stage.
We have a responsibility, as an enterprise that operates business in Japan, which consumes a significant amount of energy, to reduce reliance on finite resources and develop clean and renewable energy. In 1979, we started developing hydrogen storage alloys by applying our core technology. Subsequently, we successfully established hydrogen storage systems utilizing hydrogen storage alloys. These systems have been predominantly adopted for energy-saving and energy generation in buildings and factories. We are committed to continuing to promote sustainable energy businesses.
Products based on our technologies
Hydrogen storage and transportation
- Stationary storage containers
- Mobile storage containers for vehicles, laboratories, etc.
Application to storage and conversion technologies of thermal energy
- Thermal storage systems
- Heat pump systems for achieving high temperatures by utilizing waste heat, generating temperature gaps, etc.
- Hydrogen compressors
- Chemical engines
Other
- Purification of hydrogen gas
- Concentration and separation of deuterium
- Electrode materials for secondary batteries and fuel cells
History of hydrogen storage technology
- 1979
-
Initiated the development of hydrogen storage alloys (Iron titanium alloy was developed in collaboration with Japan Vacuum Engineering Co., Ltd. and Vacuum Metallurgical Co., Ltd.).

- 1983
-
Developed a high-efficiency heat pump system.
- 1984
-
Developed hydrogen storage alloy tanks for hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- 1986
-
Developed a hydrogen gas purification system using hydrogen storage alloys.
- 1991
-
Started the mass production of hydrogen storage alloys for nickel-hydrogen batteries.
- 1994
-
Developed hydrogen tanks for vehicles with rotary engine.
- 1997
-
Developed hydrogen tanks for fuel-cell vehicles.
- 2000
-
Developed high-capacity magnesium alloy (hydrogen storage capacity: 5.2 mass%).
- 2001
-
Developed a hydrogen supply system for UPS fuel cells.
- 2002
-
Delivered hydrogen storage systems to the first hydrogen station in Japan.

- 2004
-
Developed superlattice-type hydrogen storage alloys, contributing to the high performance of nickel-hydrogen batteries.
- 2006
-
Developed hybrid tanks for fuel-cell vehicles (FCVs).

- 2010
-
Developed high-capacity hybrid tanks (NEDO project).

- 2012
-
Delivered hydrogen systems to Iwatani Corporation (Iwatani R&D Center).

- 2013
-
Participated in a NEDO project (research and development project of hydrogen utilization technologies).
- 2014
-
Started developing high-efficiency, versatile stationary hydrogen storage systems for a hydrogen energy society.

Various applications
-

Hydrogen storage and transportation
- Stationary storage containers
- Mobile storage containers for vehicles, laboratories, etc.
-

Hydrogen storage and transportation
- Purification of hydrogen gas
- Concentration and separation of deuterium
- Electrode materials for secondary batteries and fuel cells
Hydrogen storage alloy manufacturing facility
Oguni Factory
Our hydrogen storage alloy is manufactured at the Oguni Factory of the Yamagata Plant.
-
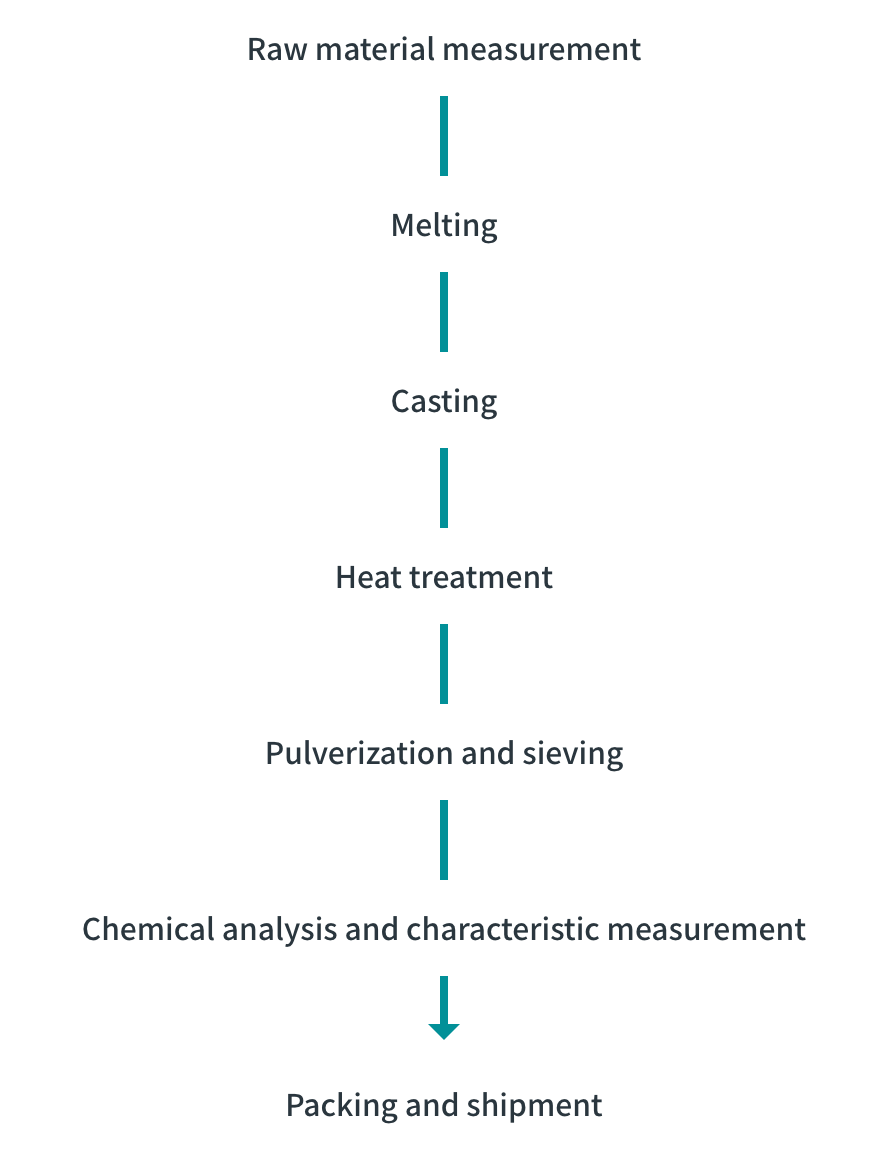
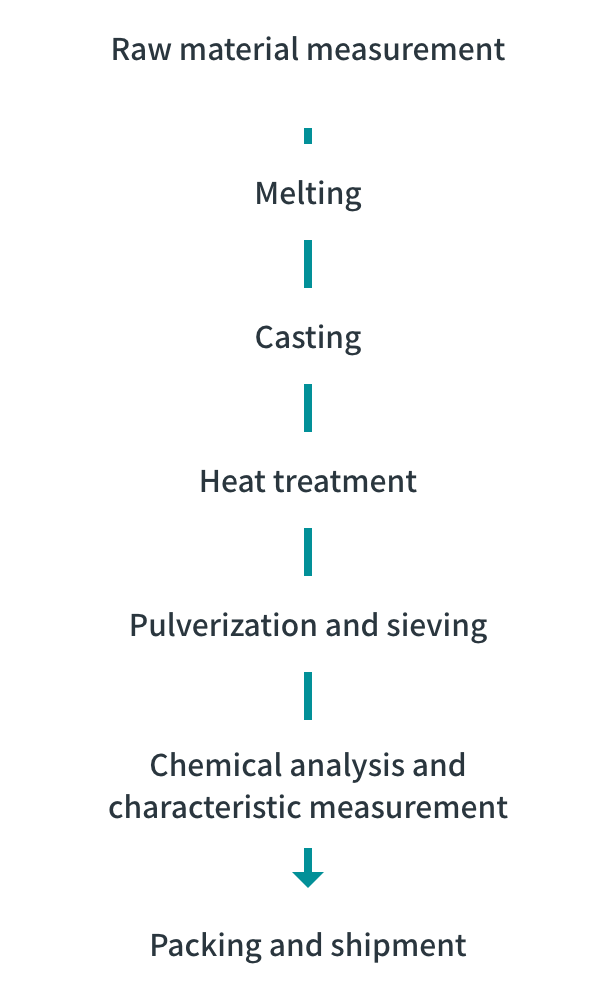
Process of producing hydrogen storage alloy