As times changed,
we were expected to produce more materials.
The business of Japan Metals & Chemicals Co., Ltd. (JMC) has expanded in various areas,
leveraging the technology it had developed in the ferroalloy field.
We provide materials required by our clients with the appropriate specifications,
while applying our core technologies of melting and pulverization to other fields.
This is how we have come to be.
Our business
originated with
- Melting
- Solidification
- Pulverization
as basic technologies.


JMC’s Business
Timeline/Milestones


JMC’s Business Timeline/Milestones
JMC has expanded its business, which began with ferroalloys, that are indispensable for steel production, with continual evolution to meet the needs of each new era.
We have supported Japanese manufacturing and paved the way for next-generation energy.
- 1938
- Ferroalloys
- 1966
- Geothermal power generation
- 1980
- Battery materials
- 1988
- High-purity metal
- 1992
- Hydrogen storage alloys
JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 溶
- 固
- 砕
“Melting, solidification, and pulverization” have been continually developed in the ferroalloy business
These core technologies are used to manufacture ferroalloys. Ferroalloys are added during the iron and steel manufacturing process to remove impurities from iron and add properties to provide metal products with various functions.
溶…Melting
固…Solidification
砕…Pulverization
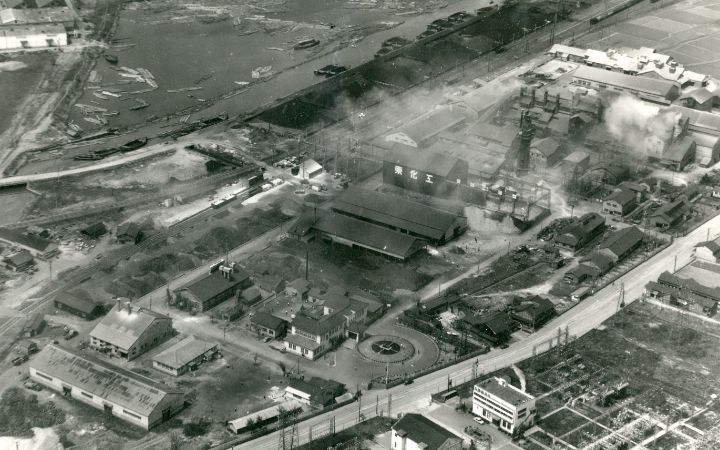
Until the 1940sOne of JMC’s predecessor companies was founded in 1917. At that time, Japan was in the midst of transition from an agricultural country to an industrial one.
Hokkai Denka Kogyo, established in the present-day Takaoka City, Toyama Prefecture, was a predecessor company of JMC, which produced carbide (calcium carbide), lime nitrogen, and ammonium sulfate. Furthermore, between 1938 and 1943, three other predecessor companies began manufacturing ferroalloys, which supported the production of steel, that was essential for postwar reconstruction.

JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 溶
- 固
- Melting
- Heat treatment
“Melting” and “heat treatment” technologies play a key role in steel casting.
This is another application of the “melting” and “solidification” technologies developed for ferroalloys.
溶…Melting
固…Solidification
From the 1950s to the 1970sJMC expanded its capacity for manufacturing ferroalloys along with the demand increase of stainless steel.
Since the production of ferroalloys requires a large amount of electricity, we pursued the construction of our own power plant. From the beginning, we have been highly conscious about protecting the natural environment, we constructed Japan’s first geothermal power plant, the Matsukawa Power Plant, in Hachimantai City, Iwate Prefecture. At that time, Japan was experiencing a period of rapid economic growth, and the heavy chemical industry was at the center of the Japanese economy. Thinking ahead in these changing times, JMC promoted corporate integration to increase its manufacturing capacity, and began ferrochrome manufacturing at the Kyushu Plant.
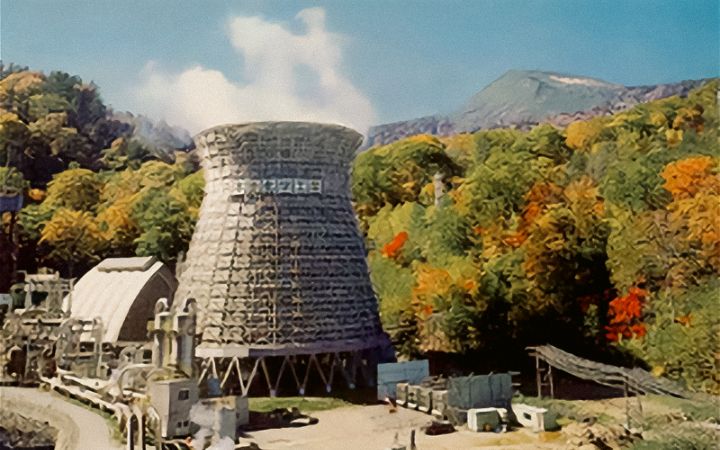 (Photo taken around 2000)
(Photo taken around 2000)
JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 電
- 電
- 電
- 電
The production of ferroalloys requires a massive amount of electricity.
Therefore, we decided to construct our own power plant. Moreover, JMC chose geothermal power generation from an ecological perspective. This led to the creation of the current energy business.
電…Electricity
JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 溶
- 砕
- Chromium
- Cobalt
The application of our core technology is possible even if we shifted from ferroalloys to non-ferrous metals such as metallic chromium and high-purity cobalt.
The production process for metallic chromium includes “pulverization” and “particle size adjustment,” while the production process for metallic cobalt includes “melting,” utilizing the technology we have developed.
溶…Melting
砕…Pulverization
JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 固
- 固
- Ceramics
- Ferrite
“Sintering” is also part of the manufacturing process of ceramics, and the heat treatment technology developed through “solidification” is utilized in this process.
Ferrite is also a ceramic material, primarily composed of iron oxide, and its manufacturing process involves “sintering.”
固…Solidification
From the 1980s to presentIn 1992, a factory for hydrogen storage alloys was completed. As JMC developed its business while foreseeing the current “environmental era” at an early stage.
Since the 1980s, automobiles and home appliances have been the primary export products of Japan. Furthermore, with the introduction of personal computers and the development of networks in each company, semiconductors came to be known as the “staple items of the industry.” JMC also responded to the demand for electronic products while constructing a plant for the production of hydrogen storage alloys. Since the 1960s, JMC has advanced its business activities with a focus on environmental conservation, and will continue to contribute to the protection of the natural environment through the use of hydrogen.

JMC’s products originated from its basic technologies
- 溶
- 固
- Battery materials
- Hydrogen storage systems
Hydrogen storage alloys were developed with the “melting” technology developed in the ferroalloy manufacturing process.
These specialty alloys have the ability to store hydrogen, and controls the absorption and release of hydrogen through the application of both “melting” and “heat treatment” technologies. The technology developed for hydrogen storage alloys is also applied to developing battery materials.
溶…Melting
固…Solidification








JMC has been committed to responding to our clients’ requests.
As a result, we have created products that satisfy a diverse range of fields and needs.
With this mindset,
JMC will continue to meet the clients’ requests.

Our Commitment

Our unchanging approach to build everlasting relationships of trust with our clients
Our Commitment

Our unchanging approach to build everlasting relationships of trust with our clients
-
01
Strive to communicate in an honest and straightforward manner.
Rather than simply saying, “We cannot do it,” we will work with the client to determine “how it can be done.” We eliminate tactics that other companies sometimes use, because they only reduce the feasibility of our high standards. We never lose sight of the fact that the present-day relationship of trust is built on such communication.
-
02
To address demand for product quality head-on
We take pride in being technology experts, and respond to clients who trust and consult with us with our technologies. In addition to honing our own core technologies, we will keep our vision on the latest technologies in the industry and examine possibilities from all aspects.
-
03
Since we are in the direct sales business, we consider expanding the scope of product development without being concerned about business size.
No one knows where the seeds of new product development lie. Since we are in the direct sales business, we must constantly strive to enhance our product lineup. We believe that consultations from our clients can lead to opportunities for us.
JMC in Figures
-
Business partners
*As of the end of February 2023
-
Sales results
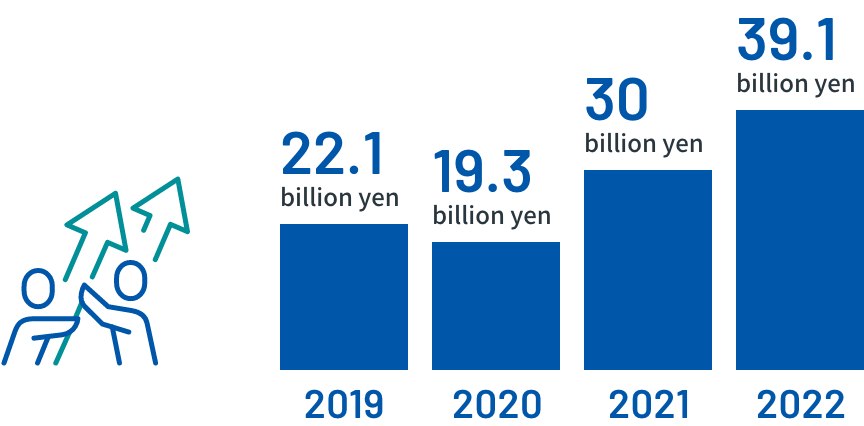
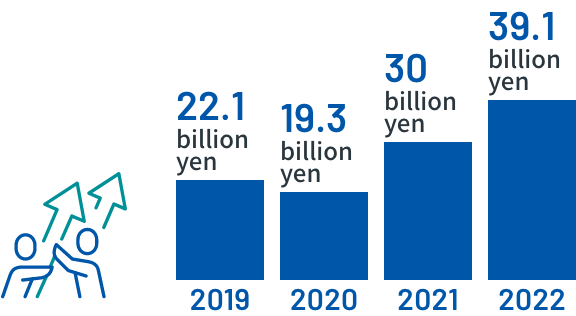
*As of the end of February 2023
*Unit: yen -
Established
-
No. of employees
*As of the end of February 2023
-
Power output
Power generated from renewable energy by JMC
-
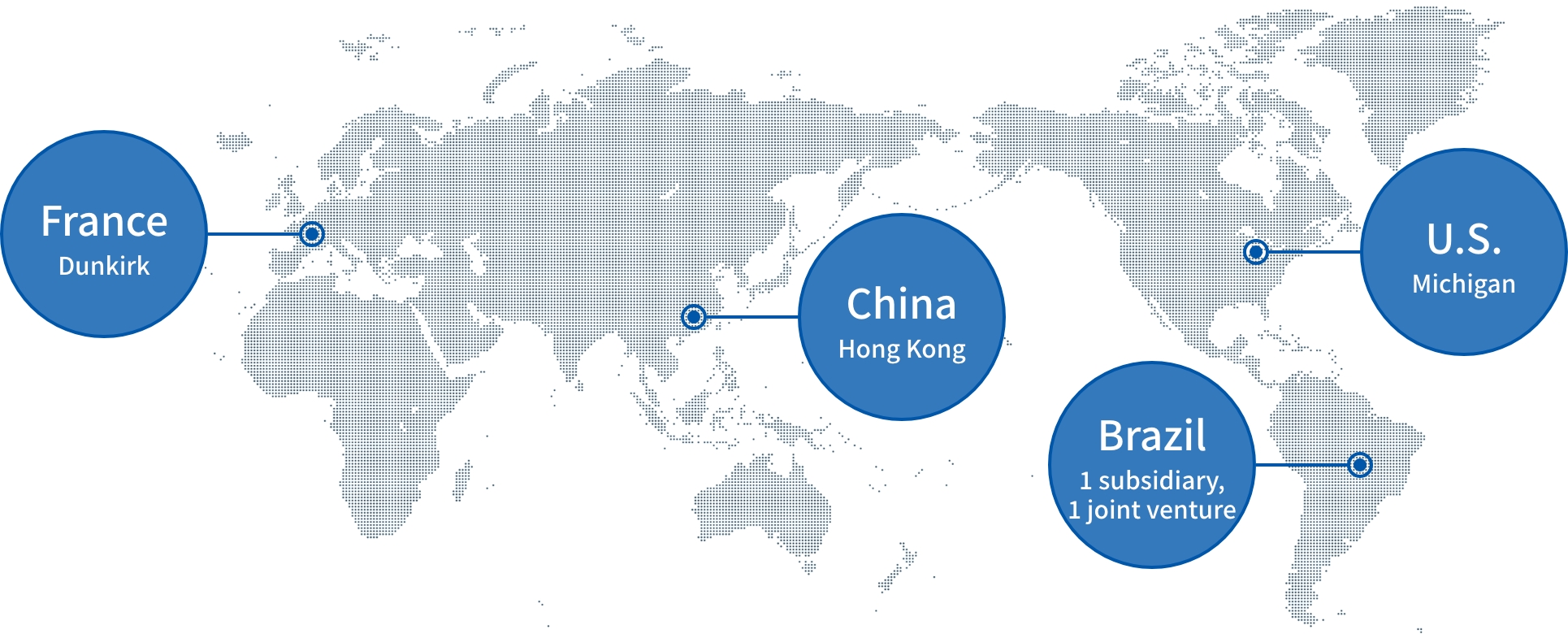
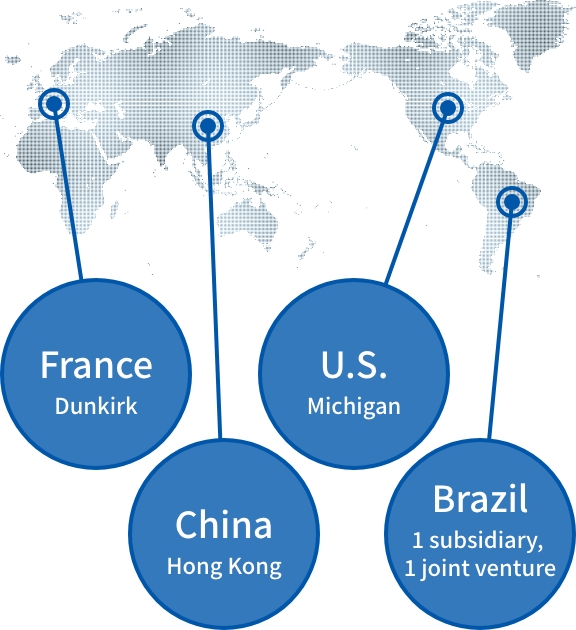
Overseas offices